Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a condition where the
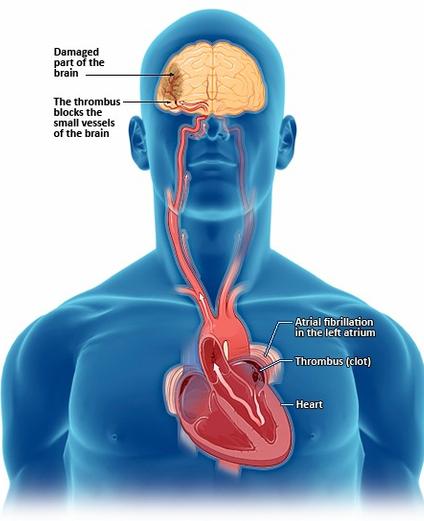
upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat irregularly and rapidly, preventing effective contractions. This irregular rhythm can cause areas of stagnant blood flow, particularly in the left atrial appendage. Stagnant blood increases the likelihood of clot formation, leading to potential complications.
If a blood clot forms in the left atrial appendage and is pumped out of the heart, it can travel to the brain, blocking circulation and causing a stroke. Individuals with AFib are 5 to 7 times more likely to suffer from a stroke compared to those without the condition. It’s estimated that over 90% of strokes in AFib patients are caused by clots in the left atrial appendage. These clots can also cause damage to other organs such as the kidneys, heart, or intestines.
To learn more about how AFib affects the heart, visit our AFib Overview page.
Assessing Stroke Risk in AFib Patients
The risk of stroke in AFib patients increases when additional factors are present. Healthcare professionals use the CHA2DS2-VASc score to estimate a patient’s annual stroke risk. The more risk factors you have, the greater your chance of experiencing a stroke. You can learn about the importance of diagnosing AFib early by visiting our Diagnosis and Risk Factors page.
Stroke Prevention Strategies
Preventing strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation involves managing the balance between clot formation and the risk of bleeding, especially for those on blood thinners. If your CHA2DS2-VASc score is two or higher, your doctor will likely recommend starting a blood thinner. However, the physician must also assess the risk of bleeding using the HAS-BLED score to make sure the benefits outweigh the risks.
Treatment Options to Lower Stroke Risk in AFib Patients
1. Blood Thinner Medications: Blood thinners are the most commonly used treatment to prevent strokes in AFib patients. Some options include:
-
- Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Newer drugs like Eliquis, Pradaxa, Savaysa, or Xarelto
To better understand medication options and management, check out our page on AFib Medications.
2. Left atrial appendage closure (LAAC): 90% of strokes in patients with AFib are caused by clots coming from the appendage. In some patients, appendage occlusion is an alternative option to reduce the risk of stroke.
The Watchman device is a minimally invasive option for patients who are unable to tolerate long-term blood thinners. While anticoagulants are effective at preventing strokes, some patients may benefit from the Watchman procedure. For more on this, explore the Left Atrial Appendage Closure (Watchman) section of our website.
Dr Jose Osorio
Miami, FL
Read More About AFib:

